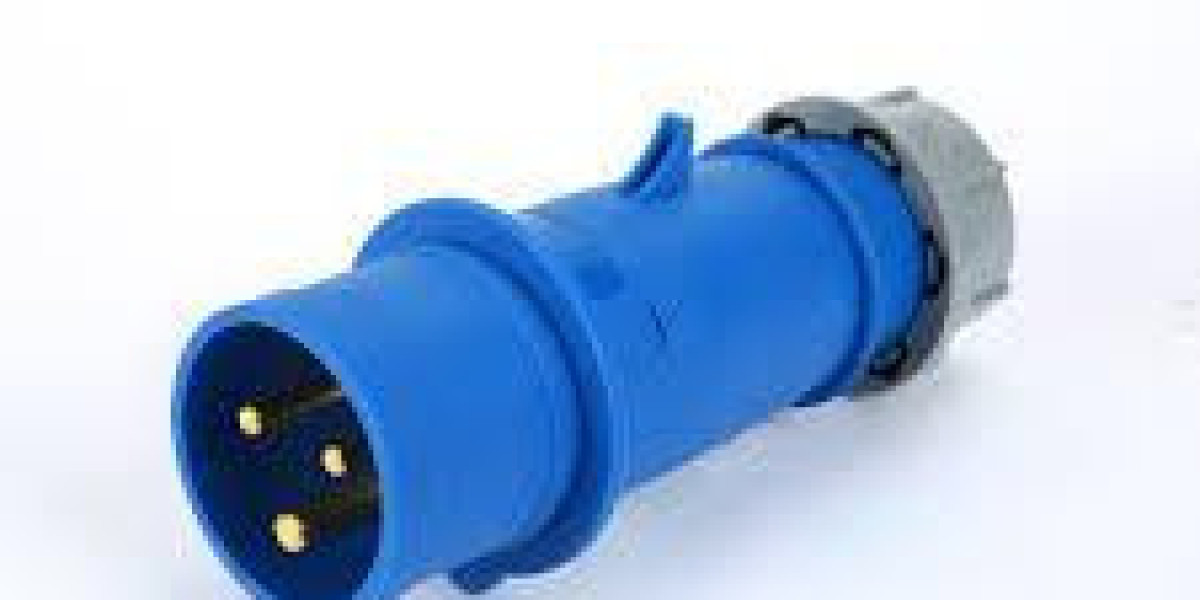
In heavy electrical installations, choosing the correct Industrial Plug early in the design process reduces rework, and experienced engineers understand that a properly specified Industrial Plug can prevent thermal hotspots, connection failures, and costly downtime. This article walks product teams and specifiers through selection logic, mechanical and electrical considerations, installation discipline, and lifecycle planning to deliver dependable connectivity for demanding industrial applications.
Define the electrical and duty profile first
Begin by quantifying the real-world electrical demands: continuous current, expected inrush (motor starts, capacitive charging), duty cycle, ambient temperature, and harmonics from non-linear loads. Connector current ratings must be interpreted with derating curves — a connector rated for a nominal current can still overheat if mounted in a poorly ventilated enclosure or repeatedly exposed to high inrush events. Specify a margin (commonly 20–30%) above expected RMS loads to allow for transient duty and future load increases.
Mechanical retention, coupling styles, and vibration resilience
Mechanical coupling choices — threaded, bayonet, or push-pull — affect how a plug resists vibration and accidental disconnection. Threaded couplers provide secure retention for permanently mounted equipment; bayonet or quick-release styles speed service for portable tools but may need supplemental locking in high-vibration settings. Look for keyed housings, anti-rotation features, and captive fasteners to avoid mis-mating and lost parts. Assess the expected mate/unmate cycles and choose hardware rated for those lifetimes to prevent premature mechanical wear.
Contact metallurgy, plating, and electrical stability
Contact material, spring geometry, and plating determine how resistance evolves over time. Copper alloys with appropriate spring temper give sustained contact force, while noble platings (silver, gold) reduce oxidation for low-current or signal contacts. For heavy-current power contacts, silver plating on a robust copper base offers an excellent compromise between conductivity and wear resistance. Request life-cycle data from suppliers showing contact resistance after thousands of cycles and under accelerated corrosion tests relevant to your environment.
Installation discipline and termination best practices
Most field failures trace back to poor terminations. Use ferrules on stranded conductors, calibrated torque tools on terminals, and strain reliefs to prevent cable movement from transmitting force to contacts. Route power and control wiring separately to minimize EMI and simplify troubleshooting. Specify clear torque values, cable-gland sizes, and sealing procedures in procurement documents and require installers to deliver as-built photos and torque logs at handover — these simple steps save hours of future diagnostics.
Environmental sealing, glands, and ingress management
Ingress protection depends on the entire assembly — connectors, glands, and enclosures. Use correctly rated cable glands tightened to manufacturer torque figures and choose gland materials compatible with chemicals and temperature excursions on site. For outdoor or washdown environments, prefer IP66/67 assemblies with robust gaskets and verify the complete system with type-test evidence. Where condensation is likely, include breathable vents, desiccants, or low-wattage thermostatic heaters to manage moisture without compromising sealing.
Thermal planning, monitoring, and preventative maintenance
Plan for thermal paths: use conductive mounting plates, oversize conductors where necessary, and arrange heat-producing equipment to avoid concentrating thermal loads near contacts. Infrared surveys during commissioning and periodic inspections catch hotspots before failures occur. For mission-critical circuits, simple temperature sensors or scheduled contact resistance checks provide leading indicators to trigger maintenance actions rather than reactive replacements.
Modular spare-part strategies and field serviceability (Nante inserts)
Design for repairability: prefer connector families with interchangeable inserts, documented compatibility matrices, and standardized spare kits. Nante-compatible modular inserts let technicians swap worn contacts or gaskets without replacing entire panels, reducing mean time to repair. Maintain a small, prioritized spare inventory (common inserts, gaskets, gland sizes) keyed to observed field failure modes to enable first-visit fixes and lower lifecycle cost.
Standards, hazardous-area considerations, and procurement language
Always demand traceable compliance with regional and international standards (IEC, UL, etc.) and require type-test reports for claimed ratings. For explosive atmospheres, ensure correct group/zone certifications and request vendor documentation during procurement. Write precise purchase specifications that call out derating expectations, life-cycle test evidence, gland torque values, and spare-kit part numbers to reduce ambiguity and supplier variation.
Thoughtful Industrial Plug selection — matching electrical profiles, mechanical coupling, contact metallurgy, installation discipline, and a compact spare strategy — turns connectors from recurring headaches into reliable, long-lived infrastructure. For technical guidance, application notes, and datasheets, visit: https://www.nante.com/news/industry-news/what-is-industrial-plug.html